Reprinted with permission of Seamanship International Ltd.
Excerpted from Chemical Tanker Notes, Published in 2006
Ballast Eductors on chemical tankers are normally installed for the purposes of stripping the segretated ballast system (not for stripping the cargo system as would be the case on conventional oil tankers as the turbulent flow could generate large static electricity accumulation in many chemical liquids).
It is recommended that the eductor be installed a short distance above the liquid to be handled and that short suction lines are used. Eductors will operate with long suction lines but, with suction lifts greater than 5 metres, capacities are reduced considerably.
When shutting down an eductor the suction valve should remain open as this prevents the eductor drawing a vacuum on the suction line.
If the eductor drive pressure falls below the designed operating pressure, the eductor suction valve should be closed to prevent any backflow of the driving liquid into the tank. The tank suction must not be used to prevent backflow as the suction pipework is not designed for such high operating pressures.
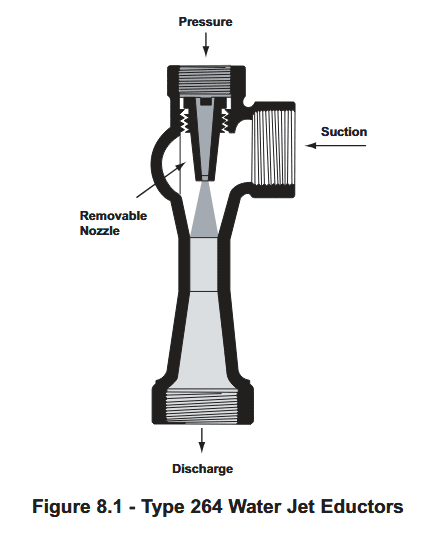
Eductors are always operated at or near their design driving pressure as a lower eductor drive fluid pressure would considerably reduce its efficiency. Sea water must always be flowing before the eductor suction valve is opened to prevent any back flow of drive fluid to the tank suction.
The eductor is operated by the drive fluid entering through the pressure nozzle, producing a high velocity jet. This jet action creates a vacuum in the line, which causes suction and the liquid to flow up the body of the eductor where it is entrained in the drive fluid. This is known as the venturi effect.
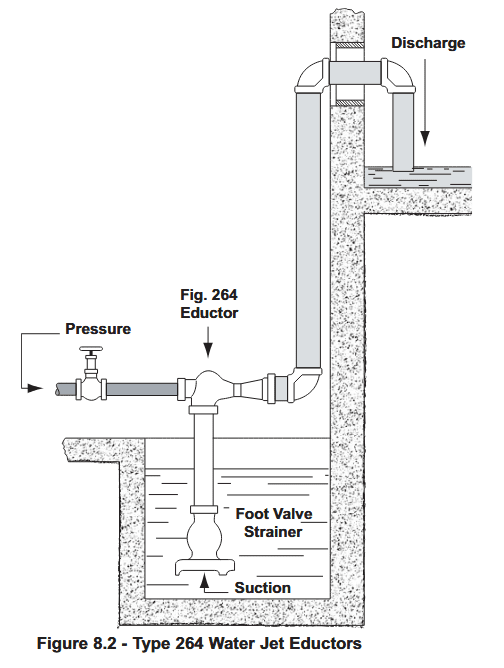
Water jet eductors are often used to empty tanks or to pump out tank and sumps. The pressure line should be fitted with a regulating stop valve and a pressure gauge while the suction line should be provided with a strainer. Discharge lines should be sealed for a positive pick-up of the liquid by turning the discharge line up or by submerging the end of the discharge line.